What Is Ovarian Cancer?
The ovaries are a pair of organs in the female reproductive system. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a fetus grows). Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond and becomes smaller through atrophy after menopause occurs. The ovaries produce eggs and female hormones (chemicals that control the way certain cells or organs function).
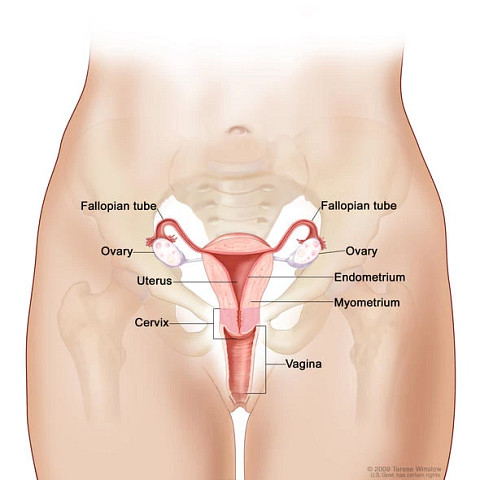
Ovarian cancer forms in the tissues of the ovary or the fallopian tube. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial carcinomas that begin in the cells from the fallopian tube or from the surface of the ovary. Cancers that arise from the peritoneal surface, called "peritoneal cancers," are treated identically to ovarian cancer and fallopian tube cancer. Malignant germ cell tumors are a type of ovarian cancer that is much less common and begins in egg cells.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for ovarian cancer can include:
- A family history of ovarian cancer: genetic risk can be transmitted between generations, either through maternal or paternal genetic inheritance. Known gene mutations that confer increased risk of ovarian cancer and other cancers include BRCA gene mutations, Lynch syndrome genes, and other gene mutations that are less common.
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Late onset of menopause
- Infertility
- Nulliparity, or a woman who has had no children
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms for ovarian cancer can include:
- Pain or swelling in the abdomen
- Gastrointestinal problems, such as gas, bloating, diarrhea, and/or constipation
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Shortness of breath
Diagnostic Tests
- Pelvic exam
- Ultrasound exam, abdominal or transvaginal; transvaginal ultrasound is able to see the ovaries much better than an abdominal ultrasound
- CA-125 assay blood test
- Biopsy
- CT (CAT) scan
Learn about how we diagnose ovarian cancer.
Treatments
Treatment options include:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC)
- Targeted therapy (for certain cases)
- Radiation therapy (for rare cases)
Learn about how we treat ovarian cancer.
Learn about clinical trials for ovarian cancer.
Factors Affecting Treatment Options and Recovery
Your prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of your cancer and whether your cancer can be operated on by a gynecologic oncology surgeon
- The subtype of ovarian cancer
- Your age and general health
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has come back (recurred)
- The genetics of your tumor